Webb telescope and Big Bang. The Webb Telescope vs. the Big Bang - who knows, perhaps the most exciting clash and crackdown on the Big Bang theory has begun - all thanks to the James Webb Space Telescope. With the end of 2022 JWST provided data from its observations, scientists analyzing the data confirmed JWST's discovery of the JADES-GS-z13-0 galaxy, which existed at the latest 320 million years after the Big Bang. Galaxies so early plus other JWST observations, caused revolutionary sentiment in the world of science.
The first surprising reports of the discovery of unusually early galaxies in the incoming data from JWST came as early as July 2022, right after the ceremonial official inauguration of this space observatory. Scientists who say they didn't expect this are probably not telling the whole truth, which is rather that they were quietly hoping for it. When they began to discover in the observational data numerous galaxies whose age, size and brightness exceeded their wildest expectations, there was great excitement in the world of astronomy and cosmology. In the months that followed, it felt as if reports of the record-breaking "earliest known galaxy" were coming in with each passing day.
After a series of revelations about surprisingly "mature" and record-breaking "early" galaxies discovered by the Webb Telescope, consternation has set in among theorists, although the first instinct was mostly skepticism. Aren't these anomalously large and bright early galaxies a coincidence, the result of some errors in the analysis of preliminary data? And if they are real, however, can they not be explained by standard cosmological models? Or are they nevertheless indications that the Universe is more complex than even our boldest theories assumed?
Many researchers believe it's a good thing that such a fuss has been created over the first JWST observations. "We are building such machines not to confirm the paradigm, but to break it," Mark McCaughrean, science and exploration advisor at the European Space Agency, said in a statement. "It's just not clear where this paradigm-breaking will lead."
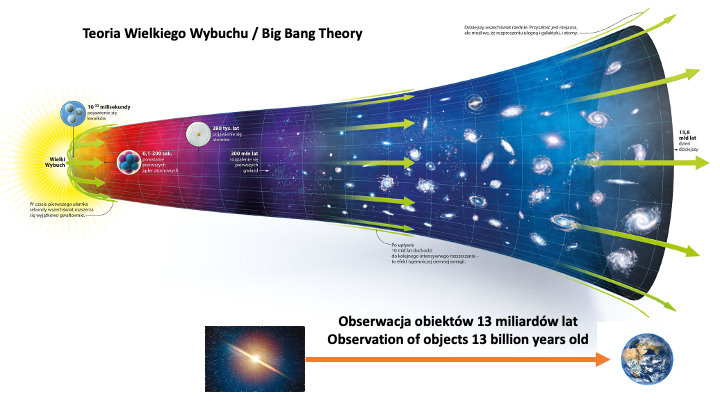
The process of observing very distant objects in time and distance is done according to the Law, which enforces the direction of observation for such objects. Observation of such objects is done in the direction of the expansion of the Universe only with an opposite turn. This means that the observer is always directed in the direction of the "Beginning" of the Universe's creation - no matter what object he or she is viewing in space this observation comes from the direction of the "Initial Singularity".
See part one of the article at the link.
Marek Ożarowski

Brak komentarzy:
Prześlij komentarz